What is heart attack and how to get rid of heart attack
What is a heart attack?
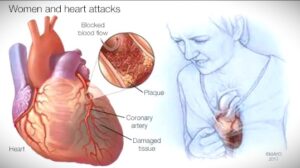
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, is the death of a part of the heart’s blood vessels. In English, it is called myocardial infarction. In English, it is called a “heart attack.”
Symptoms of heart attack disease:
- Abdominal pain, cramping, tightness or pressure.
- Pain or discomfort in the upper part of the arms, neck, back, jaw or stomach.
- Frequent breathing.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Shake your head.
- Cold sweating.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Feeling powerless or powerless.
Symptoms and signs:
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart fails to meet the demand for blood for the body’s organs and lungs. In this case, inflammation occurs in part or all of the body. It can also cause asthma and respiratory problems.
If a person lives for a long time after the failure of one of the ventricles of the heart, it can lead to the failure of both ventricles. For example, dysfunction of the left ventricle causes pulmonary edema and pulmonary hypertension that increases pressure on the right ventricle. Failure of right ventricle is not as harmful as failure of left ventricle.
Causes of heart attack disease:
Heart failure is the end result of various heart diseases. A viral infection in the heart can cause inflammation at the heart muscle level. This in turn contributes to the development of heart failure. Genetic factors play an important role in this. Heart failure is more likely to occur if multiple causes are present. Barriers to heart development, viral infections (such as HIV), and the use of drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamines increase the risk of heart failure. Constant exposure to lead and cobalt can damage the heart. Sometimes there is shortness of breath. Recent reports of patient-based trials have shown that other heart functions change with changes in blood pressure, which can provoke heart failure.
Heart attack Spread of the disease:
In 2015, heart disease affected nearly 4 million people worldwide. About 2% of adults suffer from heart disease. Between 6 and 10% of people over the age of 64 suffer from heart disease. About 10% of people over the age of 75 suffer from heart disease.
Pathology:
An overactive heart leads to increased blood flow to the heart muscle. The increase in workload over time impairs the long-term activity of neurohormonal systems such as the renin-angiotensin system. Also, fibrosis, enlargement of the ventricles, and the shape of the ventricles can vary from elliptical to spherical.
Diagnosis:
An overactive heart leads to increased blood flow to the heart muscle. As a result, the heart muscle is damaged. The increase in workload over time impairs the long-term activity of neurohormonal systems such as the renin-angiotensin system. Also, fibrosis, enlargement of the ventricles, and the shape of the ventricles can vary from elliptical to spherical.

No standard diagnostic method has been recognized for heart failure. The National Institute of Health and Care recommends measuring brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) by ultrasound.
Gender:
Men have a higher rate of heart failure, but women live longer after the onset of heart failure, so the overall prevalence rate is the same in both sexes. After menopause, women are more likely to suffer from heart failure. Women are thought to have a lower overall life expectancy than men after a diagnosis of heart disease. This can lead to diastolic disorders in women.
Directions of the research:
Some recent research suggests that maternal cell therapy may help treat heart failure. But there are studies to the contrary. which discourages the use of stem cells to treat heart failure. A 2016 study found that people treated for heart failure with bone marrow-derived stem cells had a longer life expectancy. There is also a temporary improvement in the ejection fraction of the left ventricle.
Shortness of breath can be caused by heart disease:
Shortness of breath is a physical condition when a person feels that he or she is not able to breathe well and comfortably. This is called Dyspnoea. Breathing difficulties include feelings of tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, and gasping for air.
Excessive physical exertion can cause the symptoms of normal breathing. But if a person starts having shortness of breath with a little effort, then it should be understood that the person has shortness of breath. In 85% of cases, asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, pulmonary arrhythmia, congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or psychogenic psychogenic factors such as panic disorder and anxiety.
Cessation of the heart’s activity:
A cardiac arrest is a sudden interruption of blood flow to the heart muscle. Chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea may occur before the heart stops working. As a result, the person can become unconscious or stop breathing.
Coronary artery disease is the most common cause of heart failure. Other causes include excessive bleeding, lack of oxygen, potassium deficiency, heart failure, and heavy exercise. A number of congenital heart defects can also increase the risk of long QT symptoms.
Avoid smoking, exercise, and maintain a healthy weight. Treatment includes cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and defibrillation if a shock-like pulse is found. Among those who survive, the results can be improved by managing the target temperature. Replaceable heart defibrillators can reduce the risk of recurrent death.
About 535,000 cardiac arrests occur each year in the United States, with 13 out of every 10,000 (326,000 or 61%) occurring outside of a hospital setting and the rest (209,000 or 39%) occurring inside a hospital setting. The risk of heart disease increases with age. It is more common in women than in men. The chance of recovery from emergency treatment in the hospital after cardiac arrest is about 8%. A significant percentage of those who survive have a disability. Although various American TV programs show an unrealistically high chance of recovery, as high as 67%.
Causes of cardiac arrest:
A heart attack is caused by a build-up of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the coronary arteries. As a result, blood clots break up, disrupting the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, gradually weakening the muscles of the heart wall, and eventually stopping the function of the heart. High blood pressure, too much fat in the blood, too much glucose, also help to stop the work of the heart. It could be due to shock. Due to medication, previous heart disease and mental problems.
Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation:
Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation is an emergency medical procedure used to save the life of a person who has had a heart attack (sudden stop of the heart) in which the heart is pumped (pressed to the chest) repeatedly (at least 100-120 times a minute or 2 times a second) without wasting time waiting for the help of a trained health worker, medicine or device, and often at the same time (after pressing every 30 times or 2 times every 15 seconds) artificial respiration is ensured by inserting air from the mouth to the mouth.
This is called cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). This procedure is used to ensure that the patient survives until further solutions are applied to restore spontaneous blood circulation and respiration, that the normal function of his brain remains intact, and that the heart can be restarted if possible. This procedure is recommended if a person or patient suddenly becomes breathless and stops breathing or becomes extremely abnormal (e.g. fainting).
In this case, the first thing to do is to call the emergency health service number on the phone, so that trained health workers can reach the scene as soon as possible. Cardio-pulmonary resuscitation alone does not save lives, but the procedure must be continued until health workers arrive to maximize the chances of survival. If the cardiopulmonary resuscitation method is not applied, the chances of survival of the victim per minute are significantly reduced.
Medicine:
Several medications can reduce the risk of heart failure. These include methylphenidate, tricyclic antidepressants, lithium, antipsychotics, dopamine agonists, TNF inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, salbutamol, and tamsulosin.
If you lurn more about heart attack visit the web site